Fats That Are Solid At Room Temperature And Contain No Double Bonds

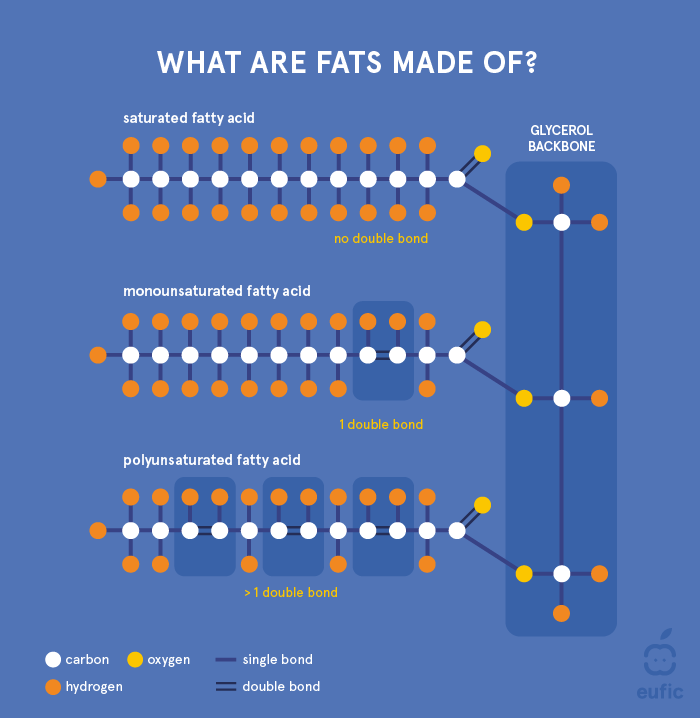
Pufas contain two or more double carbon bonds within this chain.
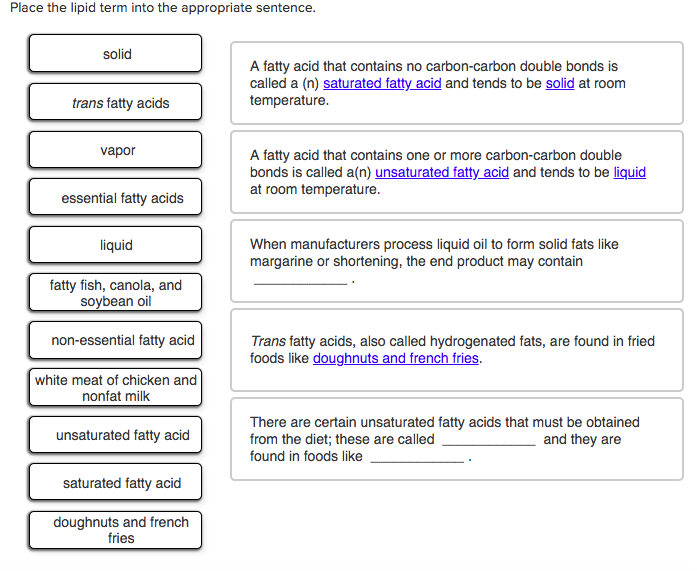
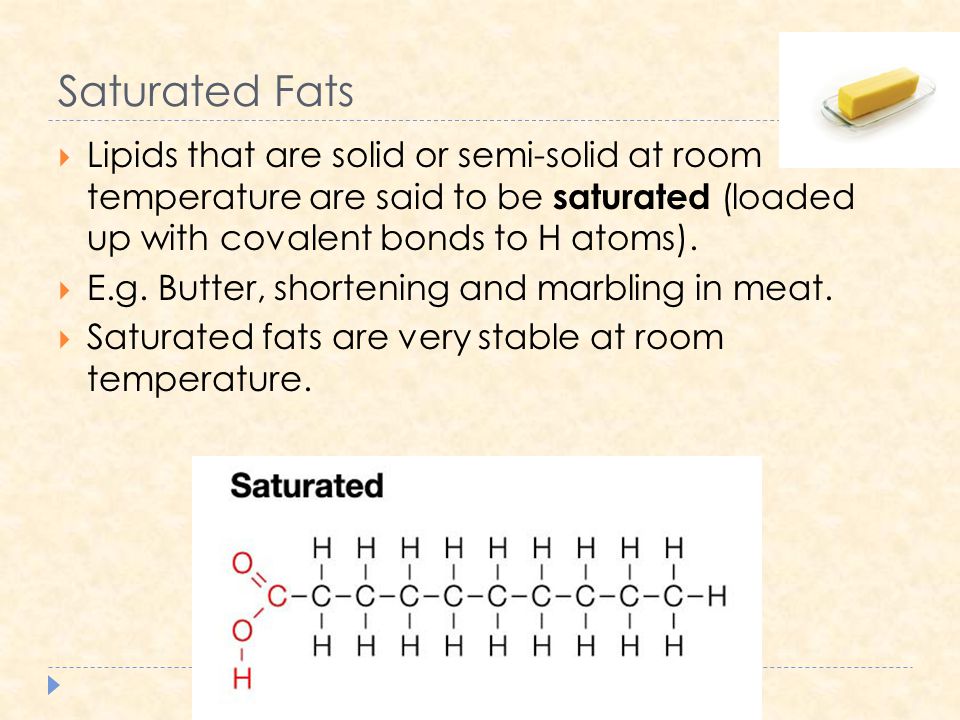
Fats that are solid at room temperature and contain no double bonds. Which contain a high percentage of saturated fats and are solid at room. Saturated fats are generally solid at room temperature. Fat hydrogenation is the process of combining fat typically vegetable oils with hydrogen in order to make it more saturated. C they contain three fatty acid tails instead of two.
Their partial hydrogenation reduces most but not all of these carbon carbon double bonds. There are some exceptions but most are solid at room temperature. Fats made up of saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature. A the double bonds in the fatty acid tails hold the molecules within the triglycerides together with more force.
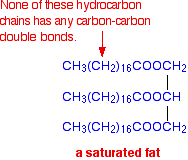
Why are saturated fats solid at room temperature. All bonds are single bonds in these fats. These types of fats include solid fat in meats as well as bacon grease. Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature.
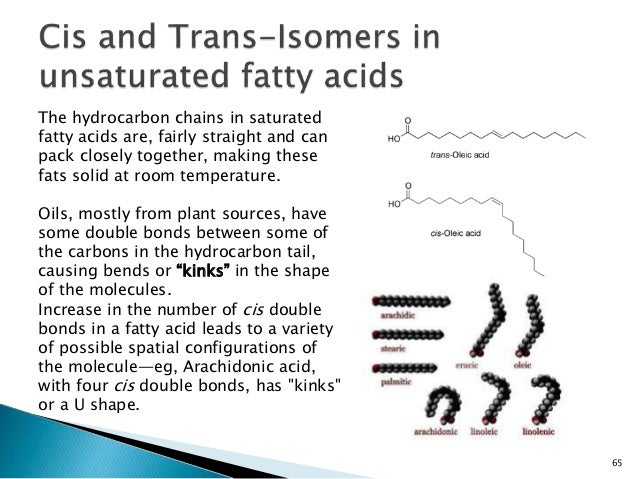
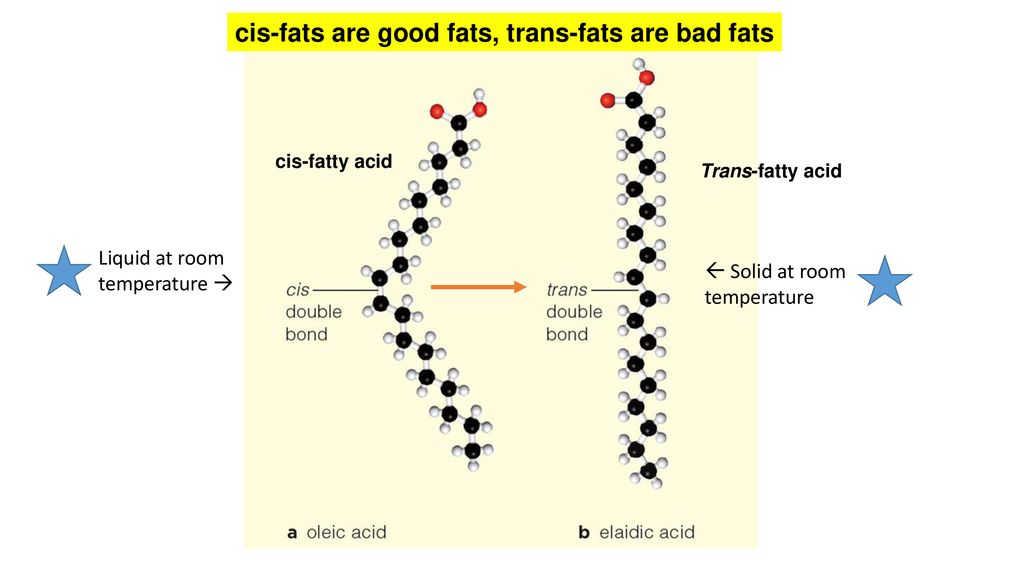
You can also see that oleic acid is not saturated. A saturated fat has no double bonds in its chemical structure whereas an unsaturated fat has one or more double bonds. They are solid at room temperature and have a high melting point compared to unsaturated fats. This fatty acid is unsaturated.
Unsaturated fats contain carbon carbon double bonds. Most animal based food contains saturated fats. Fats that are tightly packed with no double bonds between the fatty acids are called saturated fats. Unsaturated fatty acid liquid when manufacturers process liquid oil to form solid fats like margarine or shortening the end product contains.
A fatty acid that contains one or more carbon carbon double bonds is called a n and tends to be at room temperature. The process is typically carried out at very high pressure with the help of a nickel catalyst that is removed from the final product. Saturated fats are a type of fats that do not have double bonds between the molecules of fatty acid chains. Two of the carbons are connected by a double bond and two of the hydrogens are missing.
Double bonds unsaturated one double carbon carbon bond would be monounsaturated. Unsaturated fats have fewer hydrogens per carbon than a saturated fat with the same number of carbons.